It's late summer/early autumn and the floor of the coop looks like a pillow fight broke out overnight. Assuming the flock is healthy, older than 12 months, has no external parasites or other problems, they are most assuredly molting. Let's discuss what molting is, when it occurs and what can be done to help get chickens get through it efficiently.
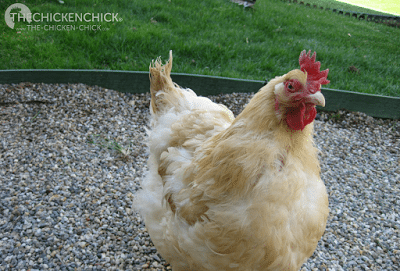
This is Phoebe, my bantam Frizzle Cochin in October 2010.
Molting is the natural shedding of old feathers and growth of new ones. Chickens molt in a predictable order beginning at the head and neck, proceeding down the back, breast, wings and tail. While molting occurs at fairly regular intervals for each chicken, it can occur at any time due to lack of water, food or sudden change in normal lighting conditions. Broody hens molt furiously after their eggs have hatched as they return to their normal eating and drinking routines.
FIRST JUVENILE MOLT
Chickens experience two, juvenile or "mini molts" as I like to call them, before a their first annual molt. The first mini molt begins at 6-8 days old and is complete by approximately 4 weeks when the chick's down is replaced by its first feathers.
SECOND JUVENILE MOLT
A chicken's second mini molt occurs between 7-12 weeks old when its first feathers are replaced by its second feathers. It is at this time that a rooster's distinguishing, ornamental feathers will appear.
ANNUAL MOLT
All chickens will molt annually, their first annual molt generally occurring around 16-18 months of age. During a molt, chickens will lose their feathers and grow new ones. Feathers consist of 85% protein and feather production places great demands on a chicken's energy and nutrient stores, as a result, egg production is likely to drop or stop entirely until the molt is finished. On average, molting takes 7-8 weeks from start to finish, but there is a wide range of normal from 4 to 12 weeks or more.
Both molting and egg production are controlled internally in response to lighting changes. When daylight hours decrease, egg production may slow down or stop completely and chickens will shed their feathers and grow new ones. When spring approaches and daytime lengthens, egg production will pick up again. At the end of summer, supplemental light may be added to the coop to promote egg-laying through the dark months.
Lucy (Easter Egger)
This is Phoebe, my White bantam frizzled Cochin, who is the poster chicken for a rough molt. She has molted in this most undignified manner for the past two years. She's a trooper though, I have yet to hear her demand a parka.
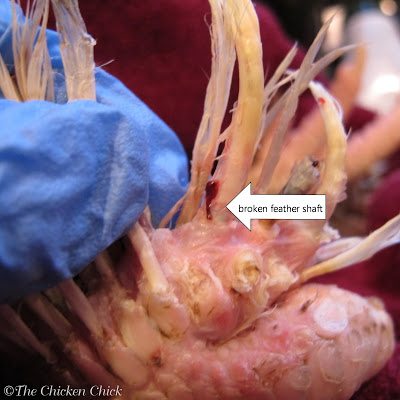
The tissue within the follicle of an emerging feather (aka: pin feather) contains a rich blood supply that will bleed if broken. Pin feathers are very sensitive and chickens generally prefer not to be handled while molting.
Feathers emerging through the vein-filled shaft, which is covered by a waxy coating (aka: the epitrichium).
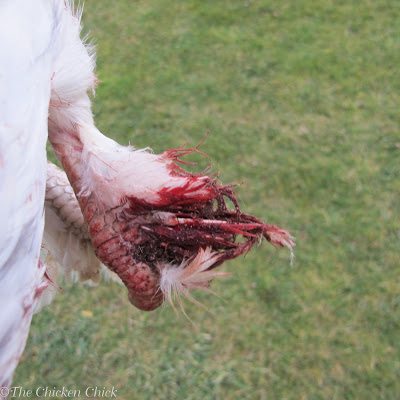
An injured feather shaft is visible in this photo as a black spot of dried blood on top of the feather shaft.
Windy is a Blue Splash Marans hen who had injured one feather shaft, which bled profusely even though the injury was minor. A bird with a bleeding pin feather should be removed from the flock for treatment and their own safety. More on how to treat an injured chicken here.
If the bleeding will not stop, the pin feather should be removed with tweezers by grasping it at the base close to the skin and pulling quickly. Apply light pressure to the area until bleeding stops. Apply a little Vetericyn Wound & Infection spray or antibiotic ointment to the area and keep the bird apart from the flock until healed.
A waxy-type casing surrounds each new feather and either falls off or is removed by a preening chicken. The feather within then unfurls and the inner blood supply dries up (the feather shaft is then known as a quill).
HOW TO HELP CHICKENS GET THROUGH A MOLT & RETURN TO EGG LAYING
There are a few things that can be done to help chickens get through a molt a little bit easier:
- Reduce their stress level as much as possible. Try not to move them to a new living quarters or introduce any new flock members during a molt.
- Change their chicken feed to a higher protein feed such as an unmedicated starter, starter/grower or a grower feed for a couple of months until the majority of the flock is over the molting hump. This dietary change is preferable to injecting their diet with high protein foods that do not consist of the correct amino acids chickens require.
- Limit handling to avoid inflicting pain and to keep stress to a minimum.
**NO MORE THAN 5% of a hen's daily dietary intake should consist of anything other than their chicken feed.** No more than 2 tablespoons per bird on any given day and not every day. Oh, and good luck ensuring that Henrietta doesn't get more than her 2 tablespoons while Matilda gets none. That's how the pecking order works. Better to skip treats entirely as they are not beneficial.
EXCESS PROTEIN ADVISORY
Caution should be exercised when supplementing the chickens' diet with protein. Large amounts of protein can lead to diarrhea and other, serious problems.
"Excess protein in a chicken's diet is converted to uric acid and deposited as crystals in joints, causing gout. The excess use of meat scraps as a source of protein can also result in an imbalance of phosphorous."1
"Incorrect diets that contain excessive levels of protein causes wetter droppings since the extra protein is converted into urates. This causes your chicken to drink more therefore you will see an increase in urates leading to wet, damp bedding."2
Remarkably, within a few weeks, dull and balding turns to shiny and voluminous.
Sources & further reading:
1 The Chicken Health Handbook, Damerow, Gail 1994 (pgs 27-28)
Mineral Deficiencies in Poultry
2 Treatment & Management of Diarrhoea
Kathy Shea Mormino
Affectionately known internationally as The Chicken Chick®, Kathy Shea Mormino shares a fun-loving, informative style to raising backyard chickens. …Read on


shop my SPONSORS
It's late summer/early autumn and the floor of the coop looks like a pillow fight broke out overnight. Assuming the flock is healthy, older than 12 months, has no external parasites or other problems, they are most assuredly molting. Let's discuss what molting is, when it occurs and what can be done to help get chickens get through it efficiently.
This is Phoebe, my bantam Frizzle Cochin in October 2010.
Molting is the natural shedding of old feathers and growth of new ones. Chickens molt in a predictable order beginning at the head and neck, proceeding down the back, breast, wings and tail. While molting occurs at fairly regular intervals for each chicken, it can occur at any time due to lack of water, food or sudden change in normal lighting conditions. Broody hens molt furiously after their eggs have hatched as they return to their normal eating and drinking routines.
FIRST JUVENILE MOLT
Chickens experience two, juvenile or "mini molts" as I like to call them, before a their first annual molt. The first mini molt begins at 6-8 days old and is complete by approximately 4 weeks when the chick's down is replaced by its first feathers.
SECOND JUVENILE MOLT
A chicken's second mini molt occurs between 7-12 weeks old when its first feathers are replaced by its second feathers. It is at this time that a rooster's distinguishing, ornamental feathers will appear.
ANNUAL MOLT
All chickens will molt annually, their first annual molt generally occurring around 16-18 months of age. During a molt, chickens will lose their feathers and grow new ones. Feathers consist of 85% protein and feather production places great demands on a chicken's energy and nutrient stores, as a result, egg production is likely to drop or stop entirely until the molt is finished. On average, molting takes 7-8 weeks from start to finish, but there is a wide range of normal from 4 to 12 weeks or more.
Both molting and egg production are controlled internally in response to lighting changes. When daylight hours decrease, egg production may slow down or stop completely and chickens will shed their feathers and grow new ones. When spring approaches and daytime lengthens, egg production will pick up again. At the end of summer, supplemental light may be added to the coop to promote egg-laying through the dark months.
Lucy (Easter Egger)
This is Phoebe, my White bantam frizzled Cochin, who is the poster chicken for a rough molt. She has molted in this most undignified manner for the past two years. She's a trooper though, I have yet to hear her demand a parka.
The tissue within the follicle of an emerging feather (aka: pin feather) contains a rich blood supply that will bleed if broken. Pin feathers are very sensitive and chickens generally prefer not to be handled while molting.
Feathers emerging through the vein-filled shaft, which is covered by a waxy coating (aka: the epitrichium).
An injured feather shaft is visible in this photo as a black spot of dried blood on top of the feather shaft.
Windy is a Blue Splash Marans hen who had injured one feather shaft, which bled profusely even though the injury was minor. A bird with a bleeding pin feather should be removed from the flock for treatment and their own safety. More on how to treat an injured chicken here.
If the bleeding will not stop, the pin feather should be removed with tweezers by grasping it at the base close to the skin and pulling quickly. Apply light pressure to the area until bleeding stops. Apply a little Vetericyn Wound & Infection spray or antibiotic ointment to the area and keep the bird apart from the flock until healed.
A waxy-type casing surrounds each new feather and either falls off or is removed by a preening chicken. The feather within then unfurls and the inner blood supply dries up (the feather shaft is then known as a quill).
HOW TO HELP CHICKENS GET THROUGH A MOLT & RETURN TO EGG LAYING
There are a few things that can be done to help chickens get through a molt a little bit easier:
- Reduce their stress level as much as possible. Try not to move them to a new living quarters or introduce any new flock members during a molt.
- Change their chicken feed to a higher protein feed such as an unmedicated starter, starter/grower or a grower feed for a couple of months until the majority of the flock is over the molting hump. This dietary change is preferable to injecting their diet with high protein foods that do not consist of the correct amino acids chickens require.
- Limit handling to avoid inflicting pain and to keep stress to a minimum.
**NO MORE THAN 5% of a hen's daily dietary intake should consist of anything other than their chicken feed.** No more than 2 tablespoons per bird on any given day and not every day. Oh, and good luck ensuring that Henrietta doesn't get more than her 2 tablespoons while Matilda gets none. That's how the pecking order works. Better to skip treats entirely as they are not beneficial.
EXCESS PROTEIN ADVISORY
Caution should be exercised when supplementing the chickens' diet with protein. Large amounts of protein can lead to diarrhea and other, serious problems.
"Excess protein in a chicken's diet is converted to uric acid and deposited as crystals in joints, causing gout. The excess use of meat scraps as a source of protein can also result in an imbalance of phosphorous."1
"Incorrect diets that contain excessive levels of protein causes wetter droppings since the extra protein is converted into urates. This causes your chicken to drink more therefore you will see an increase in urates leading to wet, damp bedding."2
Remarkably, within a few weeks, dull and balding turns to shiny and voluminous.
Sources & further reading:
1 The Chicken Health Handbook, Damerow, Gail 1994 (pgs 27-28)
Mineral Deficiencies in Poultry
2 Treatment & Management of Diarrhoea


















































Thanks! Now i know what to expect and how to help them out.
At the 2nd juvenile molt, I came out one day and thought they had been fighting and pulling each others' feathers out! I was so happy to know that they were just fine and not fighting while I was away!
Great information! I have one hen molting and she has stopped laying eggs. Flo looks odd but I love picking up her pretty feathers and making feather bouquets!She is a Campine a little skittish but curious and friends with the Buff Wyndots.
my hens are about a year and a half and there are a few that have lost there feathers and almost look scarry one a leghorn is setting and molting at the same time she's the scarriest of them and some buffs are starting they are not all molting at the same time. I really thought the rooster was pecking them but we got rid of the rooster and it is still happning so ow well to late for the rooster a beautifull ameracana i really did like him. we had a sick on that died so i've been watching… Read more »
I'm happy to know that this information was helpful to you. Thanks!
My chickens have been eating their molted feathers (any feathers lying on the ground). My guess is they're trying to recoupe any lost protein?
~Chel
Hi Chel. Molting is very demanding from a protein intake perspective. As you know from reading this blog post, we can help them get through it with a little less stress and demand on their bodies by supplementing their diet with protein. They could be eating the feathers for that reason, although I read somewhere once that feathers don't serve that purpose when eaten.